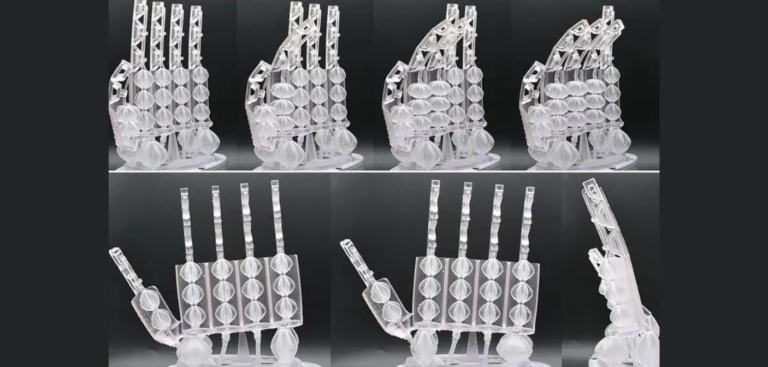
Researchers at the Italian Institute of Technology have built a 3D-printed robot hand with human-like movements, which is capable of lifting eight kilograms (17.6 lbs).
The hand was developed using actuators of 18 variant sizes.
The research team used 3D-printed artificial muscles, which were created from actuators that convert energy into movement by inflating the muscles.
“We started from the traditional artificial muscle and developed a new class of artificial muscles made of a single monolithic component,” said one researcher, Corrado De Pascali.
The small actuators within the hand are reportedly able to lift to 1,000 times their own weight. The team suggested that this development could lead to more robots with human-like hand movements.
The actuator membranes are named GeometRy-based Actuators that Contract and Elongate (GRACE) and are made using flexible resin which allows them to stretch and contract. This supports human-like movements, like twisting and bending.
The membrane was designed using a mathematical model, with actuators displaying the ability to lift a variety of heavy objects, depending on the material used in their construction. When tested, one eight gram (0.28oz) actuator lifted eight kilograms.
According to the team, what differentiates GRACE actuators from previous types are their pleated membranes, which can fold to give the artificial muscles strength and flexibility.