An ABB-sponsored report has highlighted challenges faced by car manufacturers as the transition to electrified vehicles (EVs) gathers pace, including the need to manage complexity in assembly and supply chains.
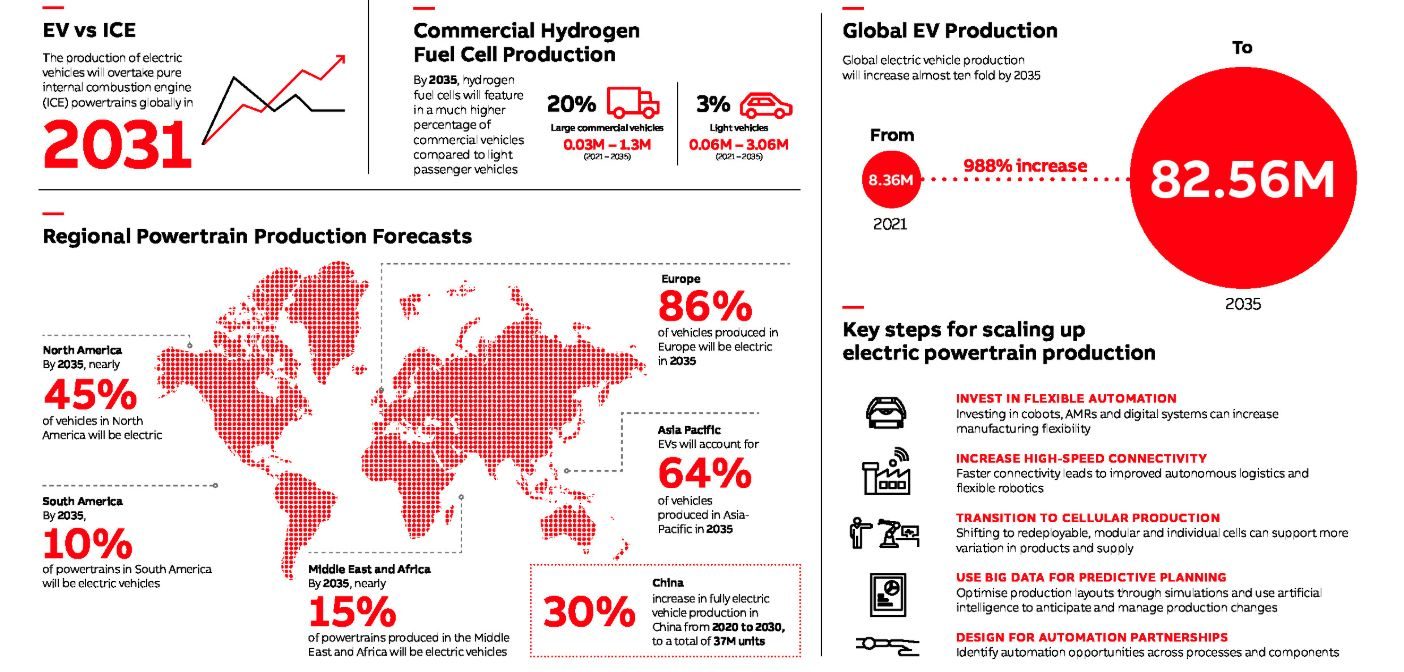
According to Flexing for the Future, a 2035 Global Powertrain Forecast Report sponsored by ABB Robotics and authored by the automotive intelligence unit of Ultima Media, car manufacturers must adopt a more flexible and collaborative approach to their production and logistics infrastructure if they are to maintain profitability and quality into the next decade.
Faced with ambitious targets for mitigating climate change together with huge regional variations in regulations and consumer attitudes, manufacturers are responding by developing platforms and production facilities that accommodate a complex mix of powertrains, from petrol and diesel to hybrid and battery-electric, as well as emerging technologies such as hydrogen fuel-cells.
The report suggests automotive manufacturers must increasingly turn to digitalisation and automation to deliver the flexibility required to manage this variety.
“By unravelling traditional long-line production architectures and deploying dedicated modular cells, manufacturers gain the ability to modify or even replace individual cells without incurring costly production interruptions,” says Joerg Reger, managing director of ABB Robotics’ automotive business.
“These zero-loss production changes allow OEMs to start small and scale up key parts of the assembly process by adding or redeploying cells as demands change. By engineering flexibility into the process, we create the means to not just manage this rising complexity, but to turn it into an opportunity.”
One of the most significant technologies in supporting this flexibility is the switch to more autonomous logistics and material handling in plants, the report suggests, with OEMs increasingly relying on autonomous mobile robots to move materials flexibly.
Furthermore, the report states that, by creating a digital twin of the facility, changes can be examined and optimised beforehand, and once a cell’s design has been optimised in the virtual space, it can be quickly rolled-out as a fully validated unit anywhere in the world.
Additionally, cellular manufacturing allows robots to be redeployed or moved to areas of high demand with a ‘lift and shift’ process, meaning an asset can extend its life beyond its original purpose, according to the report.
The report outlines that the challenge for many OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers is that their expertise tends to be concentrated in particular product technologies and manufacturing processes. It suggests the best way, therefore, to develop solutions quickly is through collaboration with a suitable external partner.
According to the report, combining the process expertise of the supplier with the automation expertise of an outside company can enable the co-creation of automation solutions in which products are not only ‘designed for manufacture’ but ‘designed for automation’.
That can lead to automation penetrating further into the production process, as evidenced by the growth in robotics use in final trim and assembly, or new technologies that remove the need for labour-intensive processes that can slow down production.
However, as the report notes, achieving flexible automation is not just a matter of acquiring robots; it requires a fresh view of how to maximise manufacturing efficiency in an uncertain and rapidly changing environment.