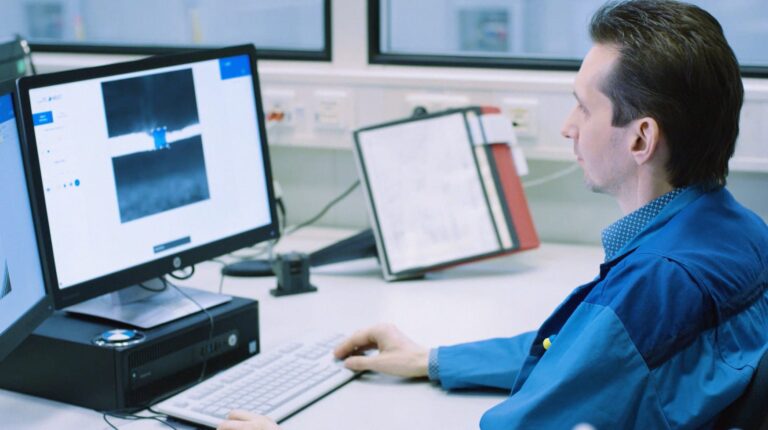
German automotive manufacturer BMW has shared numerous AI algorithms used in its production process on an open source platform.
The algorithms are part of various AI applications used for automated image recognition and image tagging.
By making these algorithms publicly available, software developers all over the world can now view, change, use and improve the source code.
Dirk Dreher, head of logistics planning, BMW, said: “With the algorithms we are now publishing, BMW has significantly reduced the development time for neural networks for autonomous transport systems and robots.”
Neural networks independently compare live images in production and logistics with hundreds of stored images in milliseconds to detect deviations from the standard.
For example, BMW uses a camera and self-learning software to check whether a warning triangle has been placed in the correct spot in the vehicle boot.

According to Kai Demtröder, head of artificial intelligence, data platforms at BMW Group IT, the open source approach benefits both interested software developers and BMW.
“We are making major investments in artificial intelligence. By sharing our algorithms with the global developer community, we want to do our part and make AI accessible to a broad group of users.
“We expect the further open source development to lead to a rapid and agile advancement of the software.”
Users of the algorithms are guaranteed anonymity by BMW. Flaws in the algorithms can be identified quickly; in this process, automated functions provided by the platform operators can also be used, if needed.
For quality assurance purposes, BMW checks all incoming user suggestions before they are put into use or shared. Furthermore, the AI application being developed with these algorithms are protected.
Users are free to decide whether they want to make their models accessible to partners, such as suppliers.
The open source platform can be accessed here.