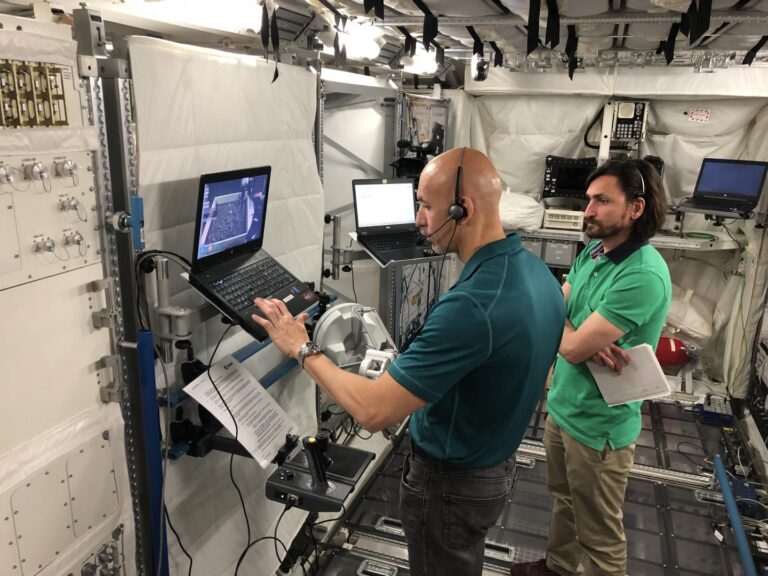
The European Space Agency (ESA) has announced that it will conduct an experiment in orbit known as ANALOG-1 to see if station crews, scientists on Earth and new technology can guide a robotic rover on a simulated lunar mission.
The project, which commences this month (November), will investigate how effectively an astronaut on the International Space Station can remotely control Moon and Mars rovers from orbit. The rover is tasked with collecting rock and soil samples, then remotely investigating the samples.
“This is a potential scientific scenario during future missions to the Moon and Mars,” said William Carey, ESA scientist and principle investigator for the ANALOG-1 experiment.
“Space is such a harsh place for humans and machines. Future exploration of the solar system may involve sending robotic explorers to test the waters on uncharted planets before sending humans.”
ANALOG-1 is the final step in ESA’s ongoing METERON (Multi-purpose End To End Robotics Operations Network) project, which is an initiative to develop and test robotics, communications and operations innovations that astronauts could use to explore the solar system.
Historically, rovers exploring other planets have been controlled with preprogrammed software and by scientists sending commands to robots from Earth.
According to the ESA, while these approaches greatly advanced its knowledge of other worlds, they also make it difficult to work fast, change plans or quickly adapt to unexpected situations.
Thus, the ESA suspects a better method may be placing astronauts in orbit around exploration sites where they could quickly communicate with the rover.
With a nearby astronaut at the rover’s controls, scientists could more efficiently explore a planned target, take advantage of a surprise opportunity or rapidly manage a problem, believes the ESA.
The results of the experiment could be of value to NASA as it prepares to explore the Moon from the planned Gateway spaceship as part of the Artemis programme, where NASA will be going forward to the Moon and on to Mars.
“A number of space agencies have looked at such a scenario for the exploration of planetary bodies – particularly for Mars,” added Carey.
“The approach could greatly increase the scientific return on those missions, as well as offer a way to avoid potential contamination from humans landing on the surface before we can answer questions about existing or previous life on Mars.”
During the two-hour experiment, ESA astronaut Luca Parmitano will use a workstation aboard the orbiting laboratory to attempt to command a remotely controllable rover and its arm while it traverses a Moon-like surface near Noordwijk, a town in the Netherlands.
Parmitano will drive the robot using a specialised computer system and will be guided by scientists communicating with him on the ground. He will also use a state-of-the-art Sigma 7 joystick that will allow the astronaut to sense what the rover’s arm encounters.
“The force feedback enables the operator to feel what the robot feels,” said ESA robotics lead engineer Thomas Krueger.
“For example, if the robot touches a fragile object, it measures and transmits information back to the user, who then feels its delicateness on the Sigma 7 joystick. They can then operate the arm more carefully than with a normal joystick.”
Parmitano will use the joystick to direct the robot’s arm to take samples of rock and soil back on Earth. Scientists expect he may face additional difficulty because of how the human body responds to space.
Research has shown that microgravity can impair an astronaut’s sense of touch or feel, as well as the ability to track moving objects – both of which are critical in this investigation’s task.
When the experiment complete, researchers on the ground will evaluate how the robotic control systems functioned and examine Parmitano’s ability to operate the rover under the effects of microgravity.
They will also observe how well Parmitano and the team on Earth were able to communicate to make decisions and plans for controlling the rover.
“Robots have the ability to extend our presence on other worlds and increase our exploration efficiency,” said ESA project manager Kjetil Wormnes. “The results of ANALOG-1 will help us determine the most effective way to collaborate with robots in order to prepare for our future exploration of the Moon.”