Copilot, which spits out code to order based on “plain English” descriptions, is a remarkable tool. But is it about to put coders out of a job?
GitHub (now owned by Microsoft) is a collaboration platform and social network for coders. You can think of it as something like a cross between Dropbox and Instagram, used by everyone from individual hobbyists through to highly paid software engineers at big tech companies.
Over the past decade or so, GitHub’s users have uploaded tens of billions of lines of code for more than 200 million apps. That’s a lot of ifs and fors and print (“hello world”) statements.
The Copilot AI works like many other machine learning tools: it was “trained” by scanning through and looking for patterns in those tens of billions of lines of code written and uploaded by members of GitHub’s coder community.
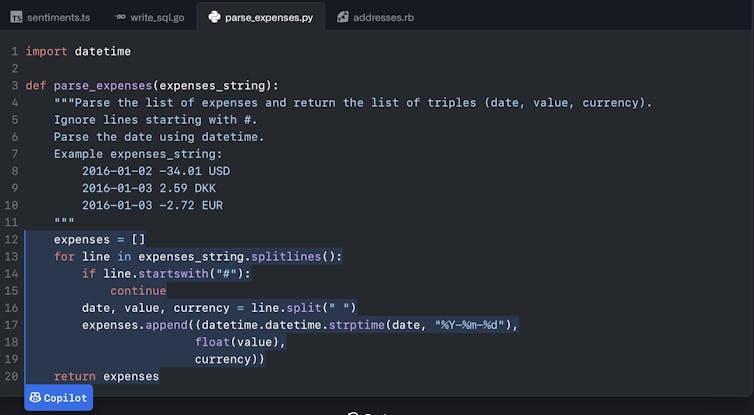
The training can take many months, hundreds of millions of dollars in computing equipment, and enough electricity to run a house for a decade. Once it’s done, though, human coders can then write a description (in plain English) of what they want their code to do, and the Copilot AI helper will write the code for them.
Based on the Codex “language model”, Copilot is the next step in a long line of “intelligent auto-completion” tools. However, these have been far more limited in the past. Copilot is a significant improvement.
A startlingly effective assistant
Copilot takes some practice to learn exactly how to frame your requests in English so the AI gives the most useful code output, but it can be startlingly effective.
However, we’re still a long way from “Hey Siri, make me a million dollar iPhone app”. It’s still necessary to use software design skills to figure out what the different bits of code should do in an app.
To understand the level Copilot is working at, imagine writing an essay. You can’t just throw the essay question at it and expect it to produce a useful, well-argued piece. But if you figure out the argument and maybe write the topic sentence for each paragraph, it will often do a pretty good job at filling in the rest of each paragraph automatically.
Depending on the type of coding being done, this can sometimes be a huge time- and brainpower-saver.
Biases and bugs
There are some open questions with these sorts of AI coding helper tools. There are worries that they’ll introduce, and reinforce, winner-takes-all dynamics: very few companies have the data (in this case, the billions of lines of code) to build tools like this, so creating a competitor to Copilot will be challenging.
And will Copilot itself be able to suggest new and better ways to write code and build software? We have seen AI systems innovate before. On the other hand, Copilot may be limited to doing things the way we’ve always done them, as AI systems trained on past data are prone to do.
Sometimes it’s trivial to see that Copilot has misunderstood an input. Those are the easy cases, and the tool makes it easy to ask for a different suggestion.
The trickier cases are where the code looks right, but it may contain a subtle bug. The bug might be because this AI code generation stuff is hard, or it might be because the billions of lines of human-written code that Copilot was trained on contained bugs of their own.
Another concern is potential issues about licensing and ownership of the code Copilot was trained on. GitHub has said it is trying to address these issues, but we will have to wait and see how it turns out.
More output from the same input
The skill many think makes them at least a little bit special may be in the process of being “automated away”, like many other jobs have been at different times in human history.
However, the human coder is still a crucial part of the system, but as curator rather than creator. Of course, you may be thinking “that’s what a coder would say” … and you may be right.
AI tools like Copilot, OpenAI’s text generator GPT-3, and Google’s Imagen text-to-image engine, have seen huge improvements in the past few years.
Many in white-collar “creative industries” which deal in text and images are starting to wrestle with their fears of being (at least partially) automated away. Copilot shows some of us in the tech industry are in the same boat.
Copilot is a force multiplier in the most optimistic tool-building tradition: it provides more leverage, to increase the useful output for the same amount of input.
These new tools and the new leverage they provide are embedded in wider systems of people, technology and environmental actors, and it’s fascinating to see how these systems reconfigure themselves in response.
In the meantime, it might help save some brain juice for the hard parts of coding work, which can only be a good thing.![]()
Ben Swift, educational experiences team lead (senior lecturer), ANU School of Cybernetics, Australian National University. This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.